antibiotic impact mycoplasma testing|Laboratory Testing for Mycoplasma pneumoniae : dealers Antibiotics may reduce clinical signs and vertical transmission but do not eliminate infection. Control requires good biosecurity, and prevention is typically through sourcing chicks or poults from M gallisepticum-free breeder flocks. . Convênios - FEMME – Laboratório da Mulher
{plog:ftitle_list}
We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us.
Perform laboratory testing when M. pneumoniae infection is suspected to ensure appropriate antibiotic therapy is administered, especially among hospitalized children. Consider swabbing both the throat and the . Clinical reference laboratories can provide diagnostic testing for Mycoplasma pneumoniae infections using culture, serology, or molecular methods. Multiple U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-cleared tests can . The global prospective surveillance data showed the re-emergence of mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia (MPP) in Europe and Asia after the coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic. We sought to observe the effect of macrolide antibiotics in the treatment of MPP carrying a macrolide-resistant mutation gene and the potential of targeted next-generation . A macrolide or tetracycline antibiotic is usually effective as first-line treatment of mycoplasma infections in both uncomplicated and more severe community-acquired pneumonia. Fluoroquinolones may be effective as .
Mycoplasma Contamination
Laboratory Testing for Mycoplasma pneumoniae
Antibiotics may reduce clinical signs and vertical transmission but do not eliminate infection. Control requires good biosecurity, and prevention is typically through sourcing chicks or poults from M gallisepticum-free breeder flocks. . INTRODUCTION. Mycoplasma pneumoniae is one of the smallest free-living organisms and a common bacterial respiratory tract pathogen. Upper respiratory tract infections and acute bronchitis are the most common manifestations of M. pneumoniae infection, but pneumonia can also occur. Manifestations outside the respiratory tract (eg, encephalitis, .
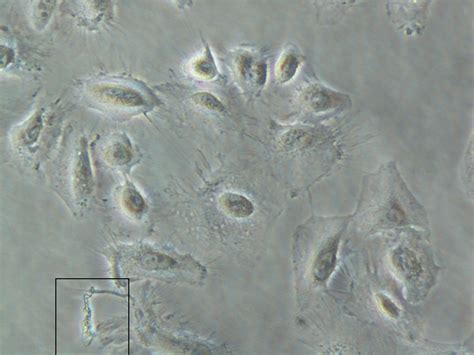
Culture supernatants and cell membranes are suitable for the growth of mycoplasma. Mycoplasmas are resistant to commonly used antibiotics and they cannot be detected visually by turbidity of fluid or under the inverted microscope. The frequency and impact of mycoplasma contamination in cell culture have been extensively discussed (12, 15-17).
M. pneumoniae are bacteria that may cause pneumonia. Mycoplasma pneumoniae is a common cause of mild respiratory illness. Since late spring, the number of infections caused by M. pneumoniae has been increasing, especially among young children.This differs from published studies in previous years, when most infections were observed among .
Ureaplasma belongs to a class of bacteria known as mycoplasma. These are the smallest self-replicating organisms known in nature and ones that tend to be commensal in the human body (meaning cohabitate with other organisms without causing damage). . genital and urinary tract but usually are well controlled by the immune system, causing little . This protocol describes these three tests for detecting Mycoplasma, which take from 1 d to 3–4 weeks, and such tests should be an obligatory component of quality control in every tissue culture .This community is for anyone looking for information and/or support regarding the STI Mycoplasma Genitalium. Feel free to discuss your experiences, symptoms, treatment outcomes, research, and more.
Clinical indications for testing. Acute, persistent and recurrent non-gonococcal urethritis . the impact of repeated courses of antimicrobials and likelihood of adverse effects needs to be balanced against the likelihood of . Time to eradication of Mycoplasma genitalium after antibiotic treatment in men and women. J Antimicrob Chemother .
Mycoplasma contamination has the potential to alter the phenotypic characteristics of the cells and can negatively impact results. Since mycoplasma is typically not visible and does not respond to antibiotics, an alternative, sensitive, and reliable detection method is required. . Reagents sufficient for 96 tests; Kit Contents. Each MycoProbe .Although the majority of M. genitalium strains are sensitive to moxifloxacin, resistance has been reported, and adverse side effects and cost should be considered with this regimen. In settings without access to resistance testing and when moxifloxacin cannot be used, an alternative regimen can be considered, based on limited data: doxycycline 100 mg orally 2 times/day for 7 .Because many antibiotics have no effect on mycoplasma, don’t indiscriminately use antibiotics to prevent contamination. . To minimize these risks, routine testing for mycoplasma is performed throughout the product manufacturing and development process. These testing methods include direct culture, indirect culture, and PCR-based detection. Australia is experiencing a current spike in respiratory infections, and cases of Mycoplasma pneumoniae or ‘walking’ pneumonia are circulating in the community, particularly among children. But with antibiotic shortages and low immunity to the infection post-pandemic, how can GPs be best prepared? Professor Adrian Esterman is Chair of Biostatistics and .
The mycoplasma PCR-ELISA test is claimed to have a detection sensitivity of 1–3 mycoplasma “particles” for particular mycoplasma species (e.g. ,M. fermentans and A. laidlawii).22 However, since for others the Limit of Detection (LOD) was 1000 “particles” per ml sample, the test does not fulfill the requirements of the EP regulatory . Here, the authors report the results of a randomised trial assessing whether adding multiplex real-time PCR to conventional testing reduces antibiotic use in community-acquired pneumonia and .Antimicrobial resistance testing and global surveillance are required to assess the efficacy of current treatment regimens and for guiding future research for the early detection and management of MDR M. genitalium infections. Keywords: Mycoplasma genitalium, non-gonococcal urethritis, antimicrobial resistance, azithromycin, moxifloxacin .
Clinical Overview of Mycoplasma pneumoniae Infection
Mycoplasma genitalium is an emerging global health threat, due to an alarming rise in antimicrobial resistance. Although individualised treatment approaches have been successfully adopted for macrolides, treatment is complicated by rising rates of fluoroquinolone resistance and by the scarcity of alternative treatment options. In this Personal View, we .
Guide to therapy . Guidelines for Mgen infections now recommend testing for macrolide resistance to help determine appropriate treatment. 11,12,13 . When applying resistance-guided therapy to a population with high levels of antibiotic resistance and cure rates below 67%, patient outcome was significantly improved. 12 Cure rates in the Mgen macrolide-susceptible .Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection - including symptoms, treatment and prevention On this page. Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection is caused by the Mycoplasma pneumoniae (M. pneumoniae).M. pneumoniae are very small bacteria with no cell walls which can cause pneumonia in humans.. How Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection is spread. Mycoplasma .
While sensitive molecular diagnostic tests enable accurate and rapid diagnosis of many respiratory viruses, their impact on antibiotic management remains uncertain, as it depends on various factors such as test type, clinical signs, site of realization (nasopharyngeal vs. endotracheal), previous antibiotic treatment, and turnaround time (TAT) [7].
Good activity of doxycycline, a tetracycline antibiotic, against Mycoplasma spp. has been described in the scientific literature [1,2, 9]. Determination of minimum inhibitory concentrations (MIC .Impact of mycoplasma contamination on cell-derived biopharmaceuticals . Mycoplasma Testing Antibiotic resistant Continue to culture Positive Secure Mycoplasma - positive aliquots as Frozen Back - up Antibiotic Treatment (e.g . BM - Cyclin ) 1. Evaluate a different antibiotic 2. Repeat treatmeent Detection and antibiotic resistance of Mycoplasma gallisepticum and Mycoplasma synoviae among chicken flocks in Egypt. . Periodic in vitro testing of MICs of antibiotics against Mycoplasma field isolates is required to monitor the impact of mass medication programs and to assist in developing effective therapies. Background Mycoplasma pneumoniae is a major cause of community-acquired pneumonia (CAP) in school-aged children. Macrolides are the first-line treatment for this infection. However, it is unclear whether macrolides are effective in treating M. pneumoniae CAP, mainly due to limitations in microbiological diagnosis of previous studies. The extensive global use of .
Impact of mycoplasma contamination on cell-derived biopharmaceuticals . Mycoplasma Testing Antibiotic resistant Continue to culture Positive Secure Mycoplasma - positive aliquots as Frozen Back - up Antibiotic Treatment (e.g . BM - Cyclin ) 1. Evaluate a different antibiotic 2. Repeat treatmeent Mycoplasma testing is used to determine whether someone currently has or recently had a mycoplasma infection. It is a group of tests that either measure anti . Mycoplasma infections often cause symptoms that resemble viral infections, but they respond to antibiotic treatment. Having a mycoplasma infection does not confer immunity. A person .
webProcedia Earth and Planetary Science, Volume 8, 2014 (2014): 10.1016/j.proeps.2014.05.013. Fiúza, António. "A Case Study on the Eco-Efficiency Performance of a Composite Processing Industry: Evaluation and Quantification of Potential Improvements". Journal of Research Updates in Polymer Science (2013):
antibiotic impact mycoplasma testing|Laboratory Testing for Mycoplasma pneumoniae